Bones of Upper limb
Region----------------Bones
Shoulder--------------Clavicle, Scapula
Arm------------------Humerus
Forearm-------------Radius, Ulna
Hand-----------Carpal bones
1)Scaphoid 2)Lunate 3)Triquetral 4)Pisiform 5)Trapezium 6)Trapezoid 7)Capitate 8)Hamate
Shoulder--------------Clavicle, Scapula
Arm------------------Humerus
Forearm-------------Radius, Ulna
Hand-----------Carpal bones
1)Scaphoid 2)Lunate 3)Triquetral 4)Pisiform 5)Trapezium 6)Trapezoid 7)Capitate 8)Hamate
Metacarpals 5, Phalanges 14 (2-3-3-3-3)
Table of Contents
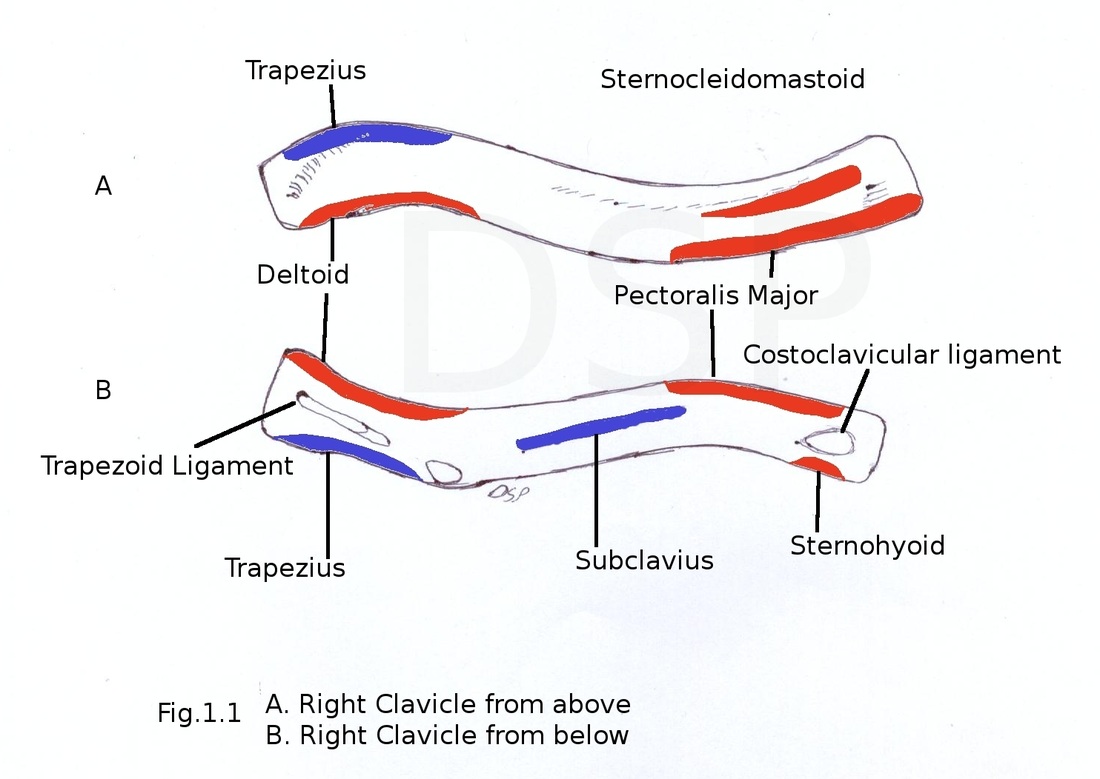
CLAVICLE
It is a long bone which lies horizontally. It articulates medially with sternum and 1st costal cartilage and laterally with acromion process of scapula.
Parts
Medial and lateral ends
Shaft
Medial end (Sternal end)
It is quadrangular and articulates with clavicular notch of manubrium sterni. It also articulates with 1st costal cartilage.
Lateral end (Acromial end)
It is flattened above downward. It shows an articular facet which articulates with acromian process of scapula.
Shaft
It is divided in to medial medial two third and lateral one third.Medial part is quadrangular in shape having four surfaces anterior, posterior, superior, inferior and inferior. Anterior surface is convex forward. Posterior surface concave backward. Superior surface is roughened. Inferior surface shows rough oval impression. Lateral part of inferior surface has a subclavian groove. A nutrient foramen is present on this inferior surface.
Lateral part is flattened from above downwards. It has two borders and two surfaces. Anterior and posterior border, superior and inferior surface. Anterior border is concave forward and posterior border is convex backward. Inferior surface has conoid tubercle and trapezoid ridge. Superior surface is subcutaneous.
Attachments
Medial end gives attachment to capsule of sternoclavicular joint along its margin, an articular disc on posterosuperior aspect and interclavicular ligament. Lateral end gives attachment to capsule of acromioclavicular joint.
Coracoclavicular ligament has conoid and trapezoid parts having attachment on conoid tubercle and trapezoid ridge respectively. Costoclavicular ligament has attachment on oval impression on inferior surface medial 2/3.Margins of subclavian groove gives attachment to Clavipectoral fascia.
Origin of muscles
Deltoid origin is on anterior border of lateral 1/3.Pectoralis major has origin on medial 2/3 of shaft. Clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid has origin on superior surface roughned medial 2/3.
Insertion of muscles
Trapezius insert on posterior border of lateral end. Subclavius is inserted into the subclavian groove on inferior surface.
Peculiarities of clavicle:
It is only long bone which lies horizontally.
It is without medullary cavity.
It is sucutaneous bone completely.
It is only long bone which ossify in membrane.
It is a long bone which has two primary centres of ossification.
It may be pierced by cutaneous nerves (Supraclavicular nerve)
Ossification:
It ossify in membrane. It ossifies from two primary centres and one secondary centre. Primary centre appear in shaft between 5th to 6th weeks of intrauterine life and fuse about 45th day of intrauterine life. The secondary centre for medial end appears during 15-17 years and fuses with shaft during 21-25 years. Sometimes a secondary centre for the lateral end which appears during 20th year and fuses within short period.
Applied anatomy:
commonest site of fracture is junction of its lateral one third and medial two third. It is the weakest point of clavicle.
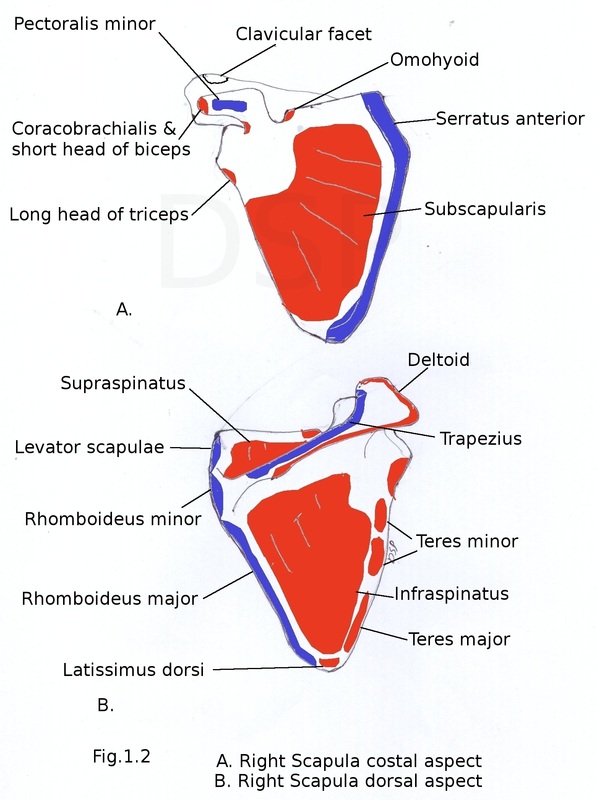
SCAPULA
Parts of scapula : Three borders, three angles, three processes, two surfaces
Surfaces:
Costal surface
Dorsal surface
Costal surface is concave directed medially and forward. It comes in relation with intercostal spaces and ribs. Three longitudinal ridges are present on this surface.
Dorsal surface is convex and divided into parts by spine of scapula a small supraspinous fossa and a large infraspinous fossa. Spinoglenoid notch present at lateral part of root of spine connecting two surfaces. Spinoglenoid notch lies near lateral angle. Suprascapular vessels and nerves pass from supraspinous to infraspinous fossa.
Borders:
Superior border
Lateral border
Medial border
Superior border is short . it present s suprascapular notch near root of coroid process. Suprascapular notch is converted into suprascapular foramen by suprascapular ligament . Suprascapular artery passes above and nerve below it.
Lateral border is thickest of all. It shows infraglenoid tubercle at its upper end. Medial border extends from superior to inferior angle.
Angles :
Superior angle
Inferior angle
Lateral angle
Superior angle lies against second rib in medial upper part of scapula. Inferior angle lies against seventh rib in lower part of scapula. Lateral angle is large broad and bears a glenoid cavity directed forward upward and laterally. Small supraglenoid tubercle is present in upper part of glenoid cavity.
Processes
Spinous process
Acromion process
Corocoid process
Spinous process is triangular plate of bone with two surfaces superior and inferior. Three borders anterior, posterior and lateral. It divides dorsal surface of scapula into supraspinous fossa and infraspinous fossa . Anterior border fixed to dorsal surface of scapula, posterior border is free called crest of spine having upper and lower lips. Lateral border forms margin of spinoglenoid notch . Acromion process has two borders medial and lateral, two surfaces superior and inferior. Medial border posses facet for clavicle and it continue as upper lip of crest of spine. Lateral border continue as lower lip of crest of spine. Coracoid process directed forward and laterally near lateral angle.
Origin of muscles:
Subscapularis arises from medial two third of subscapular fossa (costal surface). Supraspinatus arises from medial two third of supraspinous fossa. Infraspinatus arises from medial two third of infraspinous fossa. Teres minor arises from upper two third of lateral border (dorsal surface). Teres major arises from lower one third lateral border (dorsal surface). Long head of Triceps arises from infraglenoid tubercle. Deltoid arises from lower lip of crest of spine and from lateral border of acromion process. Long head of biceps arises from supraglenoid tubercle and short head from tip of coroid process lateral part. Coracobrachialis arises from tip of coroid process medial part. Inferior belly of Omohyoid arises from superior border near suprascapular notch.
Insertion of Muscles:Serratus anterior attached on costal surface medial border first digitation near superior angle, second and third digitation on a straight strip of medial border , five digitations on inferior angle. Levator scapulae inserted on medial border dorsal surface from superior angle to the apex of spine of scapula. Rhomboideus minor inserted near the apex of spine on dorsal surface of medial border. Rhomboideus major inserted on dorsal surface of medial border from area below apex of spine to inferior angle. Trapezius inserted on medial border of acromion (middle fibres) and upper lip of crest of spine (lowest fibres). Pectoralis minor inserted on upper surface and antero-medial border of corocoid process.
Other Attachments :
Coraco-acromial ligament attached to tip of acromion. Medial end of which shows attachment on postero-lateral margin of horizontal part of corocoid process. Coraco-humoral ligament attached on lateral margin of horizontal part of corocoid process just lateral to attachment of coraco-acromial ligament. Coraco-clavicular ligament trapezoid part attached on antero-medial border of corocoid process (horizontal part) and on conoid tubercle (conoid part). Glenoid labrum is attached on peripheral margin of glenoid cavity. Fibrous capsule of shoulder joint is attached on peripheral margin of glenoid cavity outside labrum.
Ossification:
It ossifies from 8 centres. One primary and seven secondary.
Primary centre for body of scapula and lower 2/3 of glenoid cavity appear in 8th week of intrauterine life.
1- corocaoid process during 1st year, 2- Subcoracoid and upper 1/3 of glenoid cavity at puberty. These fuse with body during 15-16 years.
3,4 – acromion process at puberty, 5 – medial border at puberty, 6 – inferior angle at puberty, 7 – lower margin of glenoid cavity at puberty. These fuse with body during 19-20 th year.
Applied anatomy:
Winging of scapula in which medial border of scapula is more prominent due to paralysis of serratus anterior muscle.
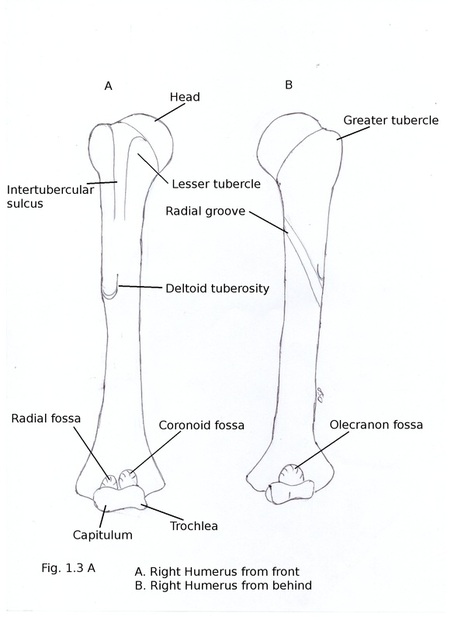
HUMERUS
Parts of Humerus:
Upper end
Lower end
Shaft
Upper end shows Head, Neck, Greater tubercle, Lesser tubercle, Inter tubercular sulcus.
Head is rounded, smooth directed medially backwards and upwards. It articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula. Neck is constriction just around head separating it from upper end. It is anatomical neck. Surgical neck is a constricted line below tubercles of upper end separating upper end from shaft. Greater tubercle is elevation on lateral part of upper end. It shows three impressions on its posterior part. Lesser tubercle is an elevation on anterior part of upper end. Inter-tubercular sulcus or bicipital groove is a vertical groove between greater and lesser tubercles. It has medial lip, lateral lip and floor.
Lower end is expanded from side to side. Capitulum is articular round projection present laterally which articulates with head of radius. Trochlea is a pulley shaped projection medially. It articulates with trochlear notch of ulna. Medial edge of trochlea extends downwards by 6mm which is responsible for carrying angle. Medial epicondyle is a projection (more prominent than lateral epicondyle ) present on medial aspect. Lateral epicondyle is a projection on lateral aspect. Medial and lateral supracondylar ridge are sharp margin present on medial and lateral side of lower end. Coronoid fossa is a depressed part on anterior aspect above trochlea. Coronoid process of ulna comes in contact with it during flexion of elbow joint. Radial fossa is similar depression on anterior aspect above capitulum. It comes in contact with head of radius during flexion of elbow joint. Olecranon fossa is a depression on posterior aspect above trochlea. It comes in contact with olecranon process of ulna during extension of elbow joint.
Shaft has three borders and three surfaces.
Borders: Anterior, Medial, Lateral
Surfaces : Anterolateral, Anteromedial, Posterior
Anterior border in upper part forms lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus. In lower part anterior border is not so sharp and becomes smooth and rounded. Lateral border in lower part forms lateral supracondylar ridge.Radial groove is present in the middle of lateral border. Medial border in upper part forms medial lip of inter-tubercular sulcus. In lower part it is continuous with medial supracondylar ridge.
Anterolateral surface is between anterior and lateral borders. Radial groove is linear depression present which goes downwards and forwards on this surface. A 'V' shaped deltoid tuberosity is present on middle part of this surface. Antero-medial surface is present between anterior and medial borders. Inter-tubercular sulcus is present in upper part of this surface. Posterior surface is between medial and lateral borders. Part of radial groove is present in middle part of this surface.
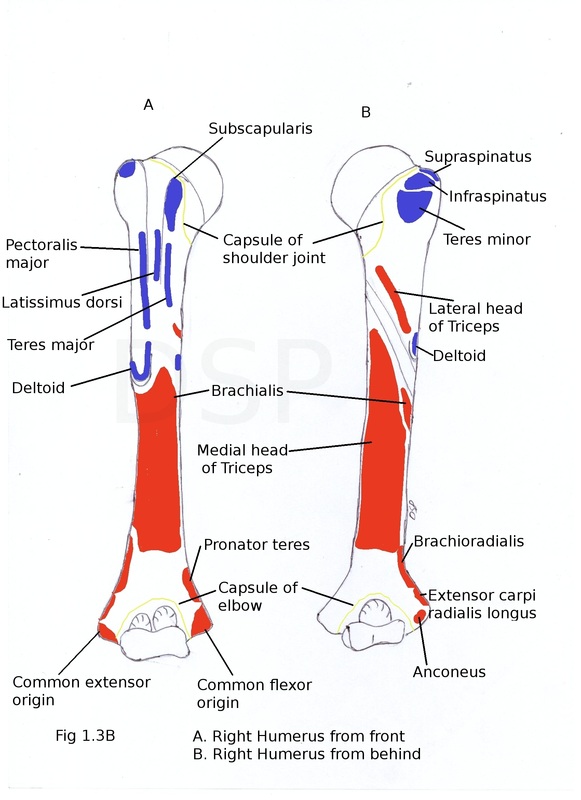
Origin of muscles:
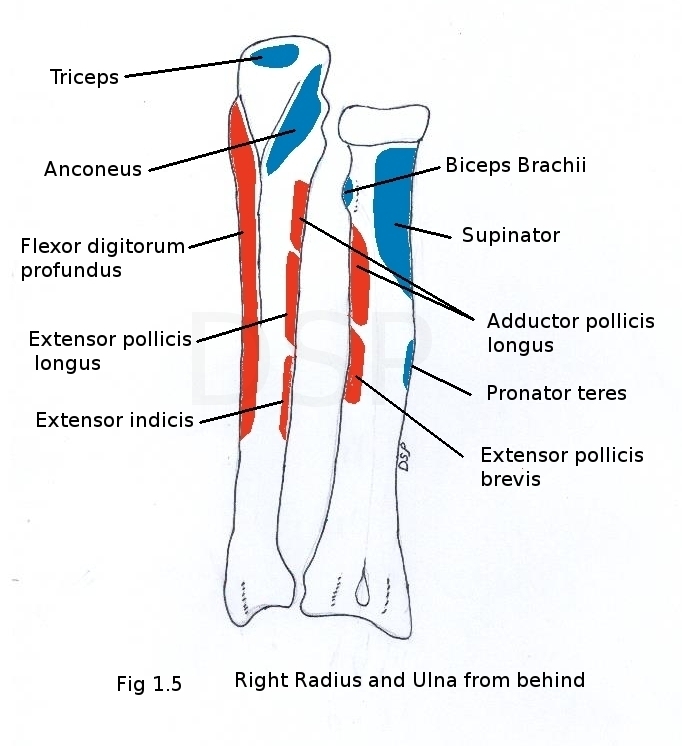
Brachialis arises from lower part of humerus antero-medial and antero-lateral surfaces of shaft. Brachioradialis and Extensor carpi radialis longus arises from upper 2/3 and lower 1/3 of lateral supracondylar ridge. Humeral head of Pronator teres arises from lower part of antero-medial surface and lower part of medial supracondylar ridge. Common extensor origin is a common origin for superficial extensor muscles of forearm. It is lateral lateral epicondyle. Common flexor origin is a common origin for Superficial flexor muscles of forearm. It is medial epicondyle anterior aspect. Anconeus originates from posterior surface of lateral epicondyle. Medial head of triceps arises from posterior surface of humerus below radial groove. Lateral head of triceps arises from a oblique line above radial groove of posterior surface.
Insertion of Muscles:
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus and Teres minor inserted on upper, middle and lower impression of greater tubercle respectively. Subscapularis inserted on lesser tubercle. Pectoralis major, Latissimus dorsi and Teres major inserted on lateral lip, floor and medial lip of inter-tubercular sulcus respectively. Deltoid inserted on deltoid tuberosity. Coracobrachialis inserted on middle of medial border.
Other Attachments :
Capsule of shoulder joint attached on anatomical neck of humerus but its lower margin extends downwards slightly on shaft. An opening is present in capsule for exit of tendon of biceps. Capsule of elbow joint attached on a line which passes above radial and coronoid fossa anteriorly and above olecranon fossa posteriorly.
Ossification:
Humerus ossify from 1 primary centre and 7 secondary centres. 1 primary centre for shaft (diaphysis) appear during 8th week of intrauterine life. 3 secondary centres for upper end 1-head, 2- greater tubercle, 3- lesser tubercle which appears during 1st, 2nd and 5th year. Fuses with each other after 5th year and with shaft after 18-19 th year. Lower end ossify from 4 centres 4- capitulum and lateral flange of trochlea, 5- medial flange of trachea, 6- lateral epicondyle, 7- medial epicondyle appears during 1st, 9th, 12th and 4th year respectively. Out of these first three fuse with each other during 13-14th year and with shaft during 15-16th year. Medial epicondyle appear as a separate epiphysis and fuses last during 18-20th year.
Applied anatomy:
- Surgical neck is the common site of fracture. Nerves which are liable for injury are Axillary nerve – near surgical neck, Radial nerve spiral groove, Ulnar nerve – behind medial epicondyle.
-Non union of fractures of humerus is common when fracture is located at the junction of upper one third and middle one third.
- Dislocation of head of humerus is common inferiorly because capsule of shoulder joint extends more below on shaft.
RADIUS
Radius present on lateral aspect of forearm.
Parts of Radius:
Upper end
Lower end
Shaft
Upper end shows head, neck and radial tuberosity. Head is rounded disc like having concave upper surface articulates with capitulum of of humerus. Peripheral smooth surface articulates medially with radial notch of ulna. Margin of it encircled by annular ligament. Neck of radius is constricted part below head. Radial tuberosity is rounded elevation below neck. Its posterior surface is rough.
Lower end is wide and shows anterior, posterior, medial, lateral and inferior surfaces. Lateral surafce projects downwards and form styloid process of radius. Medial surface shows ulnar notch for articulation with head of ulna. Anterior surface is flat and wide. Radial artery palpable here. Posterior surface shows one tubercle known as dorsal tubercle of lister. This surface shows three verticle grooves for tendons of muscles. Inferior surface is articular. It is divided into lateral triangular and medial quadrangular areas for articulation with scaphoid and lunate respectively.
Shaft shows three borders anterior, posterior and interosseous. Three surfaces anterior, posterior and lateral. Anterior border is oblique in upper part and verticle in lower part. Posterior border is predominent in middle 1/3 part. Interosseous border is also a medial border. Radial tuberosity present in its upper part. Anterior surface is between anterior and interosseous border. A nutriant foramen is present on this surface. Posterior surface is area between posterior and interosseous border. Lateral surface convex in middle part shows a rough impression for attachment of pronator teres muscle.
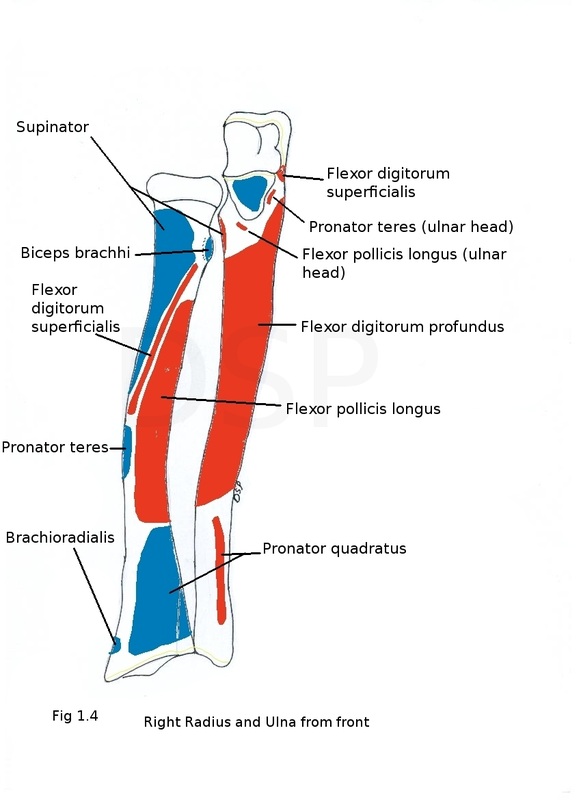
Origin of muscles:
Flexor digitorum superficialis originates from upper oblique part of anterior border. Flexor pollicis longus originates from anterior surface of shaft upper 2/3. Adductor pollicis longus and Extensor pollicis brevis originates from posterior superior surface of shaft.
Insertion of Muscles:
Supinator shows its insertion on upper end of shaft on lateral aspect. Pronator teres is inserted on lateral surface at middle of shaft. Biceps brachii is inserted on posterior rough part of radial tuberosity. Brachioradialis is inserted on lateral surface above styloid process. Pronator quadratus shows insertion on anterior surface lower part.
Other Attachments :
Quadrate ligament shows attachment on medial part of neck below annular ligament.Oblique cord shows attachment on lower end of radial tuberosity.
Ossification:
1 primary centre appears in 8th week of intrauterine life. 2 secondary centres one for lower end appears in 1st year ; second for head appears in 5th year fuses with shaft in 20th year and 18th year respectively.
Applied anatomy:
Common site of fracture is at 2cm above lower end. Colle's fracture is a fracture 2cm above lower end. Distal fragment displaces backward, upward and laterally. Dinner fork derormity of forearm is visible in this.
Non union and cross union of radius and ulna is common when both bones fractured at same time.
Smith's fracture same as Colle's fracture but distal fragment displaced forward.
Subluxation of head of radius (pulled elbow) sudden traction on head of child may cause head of radius to slip from grip of annular ligament.
ULNA
Parts:
Upper end,
Lower end
Shaft
Upper end shows Olecranon and Coronoid process, Trochlear and Radial notches. Olecranon process is a beak like process which projects upwards. Comes in contact with olecranon fossa of humerus during extension at elbow joint. It shows upper, medial, lateral, anterior and posterior surfaces. Posterior surface shows a triangular area which continue as a posterior border of shaft. Anterior surface forms upper part of trochlear notch. Medial surface continue as medial surface of shaft and coronoid process. Lateral surface continue as posterior surface of shaft. Coronoid process is a process which lie juust below olecranon process projecting forward. It shows medial, lateral, upeer and anterior surfaces. Upper surface is a lower part of trochlear notch. Anterior surface is rough and triangular shows a ulnar tuberosity in lower part. Lateral surface shows a radial notch for articulation with radial head. A supinator crest is present on this surface.
Shaft shows three borders anterior, posterior, interosseous and three surfaces anterior, posterior, medial. Anterior border starts from lower part of ulnar tuberosity to anterior part of styoid process. Posterior border is curved and subcutaneous starts from apex of a triangular subcutaneous area on back of olecranon process to posterior margin of styloid process.Interosseous border is sharp in middle part. It is continuous with supinator crest above. Anterior surface is between interosseous and anterior border. Posterior surface is between posterior and interosseous boreders. An oblique ridge divides this into upper small and lower large areas. Lower area is divided into medial and lateral part by a vertical line.
Lower end shows head of ulna and a styloid process. Head articulates with ulnar notch of radius forming inferior radioulnar joint. A articular disc is present between wrist joint and head of ulna. A styloid process is present on osteromedial side of ulna.
Origin of muscles:
Flexor carpi ulnaris shows origin from medial surface of coronoid process of ulna. Flexor digitorum profundus shows its origin from upper part of medial surface of shaft and medial surface of coronoid and olecranon process also from posterior border of shaft with an aponeurosis. Supinator shows origin from supinator crest. Flexor digitorum superficialis (ulnar head) shows origin from upper part of coronoid process. Pronator teres (ulnar head) shows origin from medial part of coronoid process. Pronator quadratus shows origin from lower one forth of anterior surface of the shaft. Extensor carpi ulnaris shows origin in middle one third part of posterior border. Abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus and extensor indicis shows its origin from posterior surface in lateral part from above downwards.
Insertion of Muscles:
Triceps brachii shows insertion on upper rough surface of olecranon process. Anconeus shows its insertion on lateral surface of olecranon process. Brachialis shows its insertion on anterior surface of coronoid process.
Other Attachments :
Annular ligament shows attachment on posterior and anterior part of radial notch. Interosseous membrane shows attachment on interosseus border. Capsular ligament of elbow joint shows attachment on trochlear notch. Oblique cord attached on radial and lower part of ulnar tuberosity direction is downwards laterally. Posterior border gives attachment to deep fascia of forearm.
Ossification:
Ulna ossifies from one primary centre and two secondary centre.1 primary centre for shaft appears in 8 week of intrauterine life. 2 secondary centres 1for lower end appears in 4th - 5th year, 1 centre for olecranon process appears in 10th year all unites with shaft in 18th year and 15 to 17 year respectively.
Applied anatomy:
Colles fracture: bone fracture about two centimetre above its lower and distal fragment is displaced upwards, backward and laterally.
Pulled elbow in this due to sudden traction on hand of child below 6 years causes dislocation of head of radius from annular ligament.
Dislocation of elbow in this 3 point relations are lost, 1 point on tip of olecranon, second and third point on medial and lateral epicondyle of humerus it forms the equilateral triangle these relations are disturbed in dislocation of elbow.
CARPAL BONES
There are 8 carpal bones in hand
proximal row : 1 scaphoid 2 lunate 3 triquetral 4 pisiform
distal row : 1 trapezium 2 trapezoid 3 capitate 4 hamate. Scaphoid is boat shaped and having tubercle laterally. Lunate is semilunar in shape . Triquetral is having a oval facet on palmar surface and its shape is wage like. Pisiform is pea shaped.Trapezium is quadrilatral in shape having a vertical groove on palmar sueface with a crest on lateral side. Trapezoid looks like a boat. Capitate is largest carpal bone with head directing a palmar surface. Hamate it is of wedge shaped bone head and hook of hamate projects anteriorly on palmar surface . Carpal bones are having 6 surfaces out of these palmar and dorsal surfaces are non articular except traquetral and pisiform. Palmer surface of triquetral articulate dorsal surface of pisiform. Dorsal surface of carpal bones are large.
Articulation:
Scaphoid articulates with radius,trapezium, trapezoid, lunate and head of capitate. Lunate articulates with radius, head of capitate, scaphoid and triquetral. Triquetral articulates with pisiform, lunate, hamate, inferior radioulnar joint (disc). Pisiform articulates with triquetral on dorsal surface. Trapezium articulates with base of first metacarpal bone forming first corpo-metacarpal joint, base of second metacarpal bone, trapezoid, scaphoid. Trapezoid articulates with capitate, trapezium, scaphoid and base of second metacarpal. Capitate articulates with hamate, trapezoid, scaphoid, lunate and 2nd, 3rd, 4th metacarpals. Hamate articulates with capitate, lunate, base of 4thand 5th metacarpal.
Scaphoid tubercle is present tubercle on lateral side. Lunate semilunar articular surface present on lateral side of bone. Triquetral shows a oval shaped facet on palmar surface. Pisiform is having articular surafce on dorsal surface. A vertical groove is present on palmar surface of trapezium lateral margin of it form a dominant crest.Trapezoid show a distal large articular surface . Head of capitate directed above and it is the largest bone. Hamate shows a hook on palmar surface.
Origin of muscles:
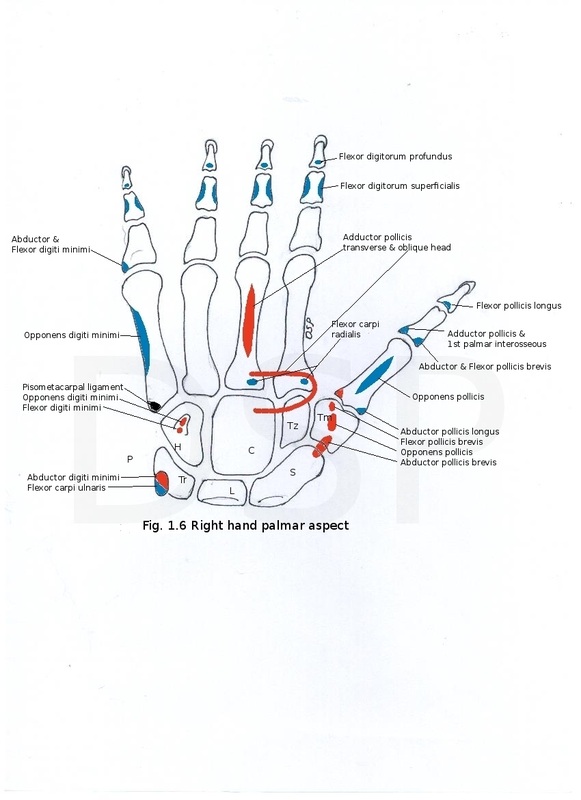
Crest on trapezium and part of scaphoid shows origin of flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis and abductor pollicis brevis respectively. Hook of hamate shows origin of flexor digiti minimi and opponens digiti minimi. Palmar surface of the trapezoid and capitate shows origin of adductor pollicis.
Insertion of Muscles:
Pisiform shows insertion of flexor carpi ulnaris on anteromedial surface.
Other Attachments :
Scaphoid tubercle shows attachment of flexor retinaculum. Pisiform shows attachment of flexor and extensor retinaculum. Trapezium shows attachment of 2 layers of flexor retinaculum in relation to groove and crest. Hook of hamate shows attachment of flexor retinaculum.
Ossification:
Carpal bones appear in a circular fashion capitate and hamate in 1st year, triquetral, lunate and scaphoid in 3rd, 4th and 5th year respectively after that trapezium, trapezoid , and pisiform in 6th, 7th and 12th year respectively.
Applied anatomy:
Scaphoid fracture: fracture of scaphoid is common. This causes avascular necrosis of scaphoid.
Anterior dislocation of lunate is common.
There are 8 carpal bones in hand
proximal row : 1 scaphoid 2 lunate 3 triquetral 4 pisiform
distal row : 1 trapezium 2 trapezoid 3 capitate 4 hamate. Scaphoid is boat shaped and having tubercle laterally. Lunate is semilunar in shape . Triquetral is having a oval facet on palmar surface and its shape is wage like. Pisiform is pea shaped.Trapezium is quadrilatral in shape having a vertical groove on palmar sueface with a crest on lateral side. Trapezoid looks like a boat. Capitate is largest carpal bone with head directing a palmar surface. Hamate it is of wedge shaped bone head and hook of hamate projects anteriorly on palmar surface . Carpal bones are having 6 surfaces out of these palmar and dorsal surfaces are non articular except traquetral and pisiform. Palmer surface of triquetral articulate dorsal surface of pisiform. Dorsal surface of carpal bones are large.
Articulation:
Scaphoid articulates with radius,trapezium, trapezoid, lunate and head of capitate. Lunate articulates with radius, head of capitate, scaphoid and triquetral. Triquetral articulates with pisiform, lunate, hamate, inferior radioulnar joint (disc). Pisiform articulates with triquetral on dorsal surface. Trapezium articulates with base of first metacarpal bone forming first corpo-metacarpal joint, base of second metacarpal bone, trapezoid, scaphoid. Trapezoid articulates with capitate, trapezium, scaphoid and base of second metacarpal. Capitate articulates with hamate, trapezoid, scaphoid, lunate and 2nd, 3rd, 4th metacarpals. Hamate articulates with capitate, lunate, base of 4thand 5th metacarpal.
Scaphoid tubercle is present tubercle on lateral side. Lunate semilunar articular surface present on lateral side of bone. Triquetral shows a oval shaped facet on palmar surface. Pisiform is having articular surafce on dorsal surface. A vertical groove is present on palmar surface of trapezium lateral margin of it form a dominant crest.Trapezoid show a distal large articular surface . Head of capitate directed above and it is the largest bone. Hamate shows a hook on palmar surface.
Origin of muscles:
Crest on trapezium and part of scaphoid shows origin of flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis and abductor pollicis brevis respectively. Hook of hamate shows origin of flexor digiti minimi and opponens digiti minimi. Palmar surface of the trapezoid and capitate shows origin of adductor pollicis.
Insertion of Muscles:
Pisiform shows insertion of flexor carpi ulnaris on anteromedial surface.
Other Attachments :
Scaphoid tubercle shows attachment of flexor retinaculum. Pisiform shows attachment of flexor and extensor retinaculum. Trapezium shows attachment of 2 layers of flexor retinaculum in relation to groove and crest. Hook of hamate shows attachment of flexor retinaculum.
Ossification:
Carpal bones appear in a circular fashion capitate and hamate in 1st year, triquetral, lunate and scaphoid in 3rd, 4th and 5th year respectively after that trapezium, trapezoid , and pisiform in 6th, 7th and 12th year respectively.
Applied anatomy:
Scaphoid fracture: fracture of scaphoid is common. This causes avascular necrosis of scaphoid.
Anterior dislocation of lunate is common.
Metacarpal bones
These are 5 miniature long bones of hand numbered from lateral to medial side. Parts head, shaft, base. Head forms knuckles of the hand. Head is articular articulating with base of proximal phalanx. Articular surface extends more on palmar part.
Shaft shows a triagular area on its dorsal surface apex towards the base. Palmar surface is concave proximo distally.
Base of metacarpal is irregular articulating with distal row of carpal bones.
Other characters of metacarpal bones.1. It is a shortest and stoutest metacarpal bone. Its base is concavo-convex for articulation with trapezium. Its head shows medial and lateral tubercle. Lateral tubercle is more prominent. Sesamoid bone lies here.
2. It is a longest metacarpal bone. Its base shows of groove. Medial lip of the groove is prominent. Medial side of the base shows an articular strip.
3. It shows a styloid process on dorsal surface on it lateral part. Lateral side of the base shows an articular strip.
4. A single quadrilateral facet present on proximal part of its base. Two small facets present on lateral side and a strip like facet on medial side.
5. It shows a nonarticular prominent tubercle on medial side and a strip like articular facet on lateral side.
Origin of muscles, Insertion of Muscles, Other Attachments:
1. Anterolateral area of shaft shows insertion of opponens pollicis. Ulnar side of the base shows origin of first palmar interosseous muscle. Anteromedia area of the shaft shows origin of first dorsal interosseous muscle. Abductor pollicis longus shows insertion on lateral side of base.
2. Anterolateral and anteromedial area of the shaft shows origin of ulnar head of first dorsal interosseous and radial head of second dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. A slip of flexor carpi radialis inserted on palmar surface of the base. Anteromedial surface of the shaft shows origin of 2nd palmer interosseous muscle. Dorsal surface of the base shows insertion of extensor carpi radialis longus. Oblique head of the adductor pollicis shows origin from palmar surface near base.
3. Anterolateral and anteromedial surface of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of second dorsal interosseous and radial head of third dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. A slip of flexor carpi radialis shows insertion near base on its palmar surface. Transverse head of adductor pollicis shows origin from verticle ridge on palmar surface of shaft. Extensor carpi radialis brevis show insertion near base on its dorsal surface. Oblique head of adductor pollicis shows origin from base near palmar surface.
4. Anterolateral and anteromedial surfaces of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of third dorsal interosseous and radial head of 4th dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. Anterolateral area of palmar surface of shaft also shows origin of the third palmar intraosseous muscle.
5. Anterolateral surface of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of 4th dorsal interosseous and also origin of 4th palmar interosseous muscles.Opponens digiti minimi shows insertion on anteromedial surface of shaft.Extensor carpi ulnaris shows insertion base of tubercle.
Ossification:
1 primary centre for shaft. secondary centres for the head of 2nd to 5th metacarpal and base of first metacarpal. Secondary centre appear during second year and fuses with shaft after 15th to 18th year.
Applied anatomy:
Bennett's fracture fracture at the base of the first metacarpal. Tuberculosis or Syphilis of metacarpal occurred in the middle of metacarpal.
PHALANGES
Number in each hand are 14, 3 for medial 4 fingers and 2 for thumb.Phalanges are proximal, middle and distal. Each phalanx shows base, shaft and head.
Base of proximal phalanx is concave for articulation with head of metacarpal bone. Bases of middle and distal phalanges shows two concave facets. Shaft phalanx is convex transversely on its dorsal surface. Palmar surface of phalanx is flat side to side and slightly concave below upwards. Heads of proximal and middle phalanges are pulley like for articulation with other phalanges. The head of distal phalanx shows a horse shoe shaped tuberosity on its palmar aspect.
Attachments:
Distal phalanges of medial 4 fingers show the insertion near base on palmar surface of flexor digitorum profundus and on dorsal surface near base insertion of dorsal digital expansion. Distal phalanx of first finger shows insertion of flexor pollicis longus on palmar surface and extensor pollicis longus on dorsal surface near base. Middle phalanx on both side shows insertion of flexor digitorum superficialis, dorsal surface near base shows insertion of dorsal digital expansion. Fibrous flexor sheath show the attachment on both side of shaft in middle and proximal phalanx. Base of proximal phalanx shows insertion of the lumbricals and interossei muscles on both side. Base of the thumb shows insertion of following structures abductor pollicis brevis and flexor pollicis brevis on lateral side, extensor pollicis brevis on dorsal surface and adductor pollicis with 1st palmar interosseus muscle on medial side. Base of proximal phalanx of 5th finger shows insertion of abductor digiti minimi and flexor digital minimi on medial side.
Ossification :
Primary centre for phalanges appear in 10th week and 11 week and 8th week of intrauterine life for proximal phalanx, middle phalanx and distal phalanx respectively. Secondary centre for base of phalanx appear in second to third year. All the centre fuse with each other during 16 to 18 years of life.
These are 5 miniature long bones of hand numbered from lateral to medial side. Parts head, shaft, base. Head forms knuckles of the hand. Head is articular articulating with base of proximal phalanx. Articular surface extends more on palmar part.
Shaft shows a triagular area on its dorsal surface apex towards the base. Palmar surface is concave proximo distally.
Base of metacarpal is irregular articulating with distal row of carpal bones.
Other characters of metacarpal bones.1. It is a shortest and stoutest metacarpal bone. Its base is concavo-convex for articulation with trapezium. Its head shows medial and lateral tubercle. Lateral tubercle is more prominent. Sesamoid bone lies here.
2. It is a longest metacarpal bone. Its base shows of groove. Medial lip of the groove is prominent. Medial side of the base shows an articular strip.
3. It shows a styloid process on dorsal surface on it lateral part. Lateral side of the base shows an articular strip.
4. A single quadrilateral facet present on proximal part of its base. Two small facets present on lateral side and a strip like facet on medial side.
5. It shows a nonarticular prominent tubercle on medial side and a strip like articular facet on lateral side.
Origin of muscles, Insertion of Muscles, Other Attachments:
1. Anterolateral area of shaft shows insertion of opponens pollicis. Ulnar side of the base shows origin of first palmar interosseous muscle. Anteromedia area of the shaft shows origin of first dorsal interosseous muscle. Abductor pollicis longus shows insertion on lateral side of base.
2. Anterolateral and anteromedial area of the shaft shows origin of ulnar head of first dorsal interosseous and radial head of second dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. A slip of flexor carpi radialis inserted on palmar surface of the base. Anteromedial surface of the shaft shows origin of 2nd palmer interosseous muscle. Dorsal surface of the base shows insertion of extensor carpi radialis longus. Oblique head of the adductor pollicis shows origin from palmar surface near base.
3. Anterolateral and anteromedial surface of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of second dorsal interosseous and radial head of third dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. A slip of flexor carpi radialis shows insertion near base on its palmar surface. Transverse head of adductor pollicis shows origin from verticle ridge on palmar surface of shaft. Extensor carpi radialis brevis show insertion near base on its dorsal surface. Oblique head of adductor pollicis shows origin from base near palmar surface.
4. Anterolateral and anteromedial surfaces of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of third dorsal interosseous and radial head of 4th dorsal interosseous muscles respectively. Anterolateral area of palmar surface of shaft also shows origin of the third palmar intraosseous muscle.
5. Anterolateral surface of shaft shows origin of ulnar head of 4th dorsal interosseous and also origin of 4th palmar interosseous muscles.Opponens digiti minimi shows insertion on anteromedial surface of shaft.Extensor carpi ulnaris shows insertion base of tubercle.
Ossification:
1 primary centre for shaft. secondary centres for the head of 2nd to 5th metacarpal and base of first metacarpal. Secondary centre appear during second year and fuses with shaft after 15th to 18th year.
Applied anatomy:
Bennett's fracture fracture at the base of the first metacarpal. Tuberculosis or Syphilis of metacarpal occurred in the middle of metacarpal.
PHALANGES
Number in each hand are 14, 3 for medial 4 fingers and 2 for thumb.Phalanges are proximal, middle and distal. Each phalanx shows base, shaft and head.
Base of proximal phalanx is concave for articulation with head of metacarpal bone. Bases of middle and distal phalanges shows two concave facets. Shaft phalanx is convex transversely on its dorsal surface. Palmar surface of phalanx is flat side to side and slightly concave below upwards. Heads of proximal and middle phalanges are pulley like for articulation with other phalanges. The head of distal phalanx shows a horse shoe shaped tuberosity on its palmar aspect.
Attachments:
Distal phalanges of medial 4 fingers show the insertion near base on palmar surface of flexor digitorum profundus and on dorsal surface near base insertion of dorsal digital expansion. Distal phalanx of first finger shows insertion of flexor pollicis longus on palmar surface and extensor pollicis longus on dorsal surface near base. Middle phalanx on both side shows insertion of flexor digitorum superficialis, dorsal surface near base shows insertion of dorsal digital expansion. Fibrous flexor sheath show the attachment on both side of shaft in middle and proximal phalanx. Base of proximal phalanx shows insertion of the lumbricals and interossei muscles on both side. Base of the thumb shows insertion of following structures abductor pollicis brevis and flexor pollicis brevis on lateral side, extensor pollicis brevis on dorsal surface and adductor pollicis with 1st palmar interosseus muscle on medial side. Base of proximal phalanx of 5th finger shows insertion of abductor digiti minimi and flexor digital minimi on medial side.
Ossification :
Primary centre for phalanges appear in 10th week and 11 week and 8th week of intrauterine life for proximal phalanx, middle phalanx and distal phalanx respectively. Secondary centre for base of phalanx appear in second to third year. All the centre fuse with each other during 16 to 18 years of life.
FAQs
Name of first ossifying bone is.?
Clavicle bone.
Spinous,acromion,coracoid processes in which bone.?
Scapula bone.
Feature of dorsal surface of scapula.?
Convex,supraspinatous fossa 1/3rd & infraspinatous fossa 2/3rd.